#Load all libraries needed
library(geofacet)
library(glmnet)
## Loading required package: Matrix
## Loaded glmnet 4.1-8
library(usmap)
library(ggpubr)
## Loading required package: ggplot2
library(ggthemes)
library(haven)
library(kableExtra)
library(maps)
library(mgcv)
## Loading required package: nlme
## This is mgcv 1.9-1. For overview type 'help("mgcv-package")'.
library(mgcViz)
## Loading required package: qgam
## Registered S3 method overwritten by 'GGally':
## method from
## +.gg ggplot2
## Registered S3 method overwritten by 'mgcViz':
## method from
## +.gg GGally
##
## Attaching package: 'mgcViz'
## The following objects are masked from 'package:stats':
##
## qqline, qqnorm, qqplot
library(RColorBrewer)
library(scales)
library(sf)
## Linking to GEOS 3.11.0, GDAL 3.5.3, PROJ 9.1.0; sf_use_s2() is TRUE
library(spData)
## To access larger datasets in this package, install the spDataLarge
## package with: `install.packages('spDataLarge',
## repos='https://nowosad.github.io/drat/', type='source')`
library(stargazer)
##
## Please cite as:
## Hlavac, Marek (2022). stargazer: Well-Formatted Regression and Summary Statistics Tables.
## R package version 5.2.3. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=stargazer
library(tidygeocoder)
library(tidyverse)
## ── Attaching core tidyverse packages ──────────────────────── tidyverse 2.0.0 ──
## ✔ dplyr 1.1.4 ✔ readr 2.1.5
## ✔ forcats 1.0.0 ✔ stringr 1.5.1
## ✔ lubridate 1.9.3 ✔ tibble 3.2.1
## ✔ purrr 1.0.2 ✔ tidyr 1.3.1
## ── Conflicts ────────────────────────────────────────── tidyverse_conflicts() ──
## ✖ readr::col_factor() masks scales::col_factor()
## ✖ dplyr::collapse() masks nlme::collapse()
## ✖ purrr::discard() masks scales::discard()
## ✖ tidyr::expand() masks Matrix::expand()
## ✖ dplyr::filter() masks stats::filter()
## ✖ dplyr::group_rows() masks kableExtra::group_rows()
## ✖ dplyr::lag() masks stats::lag()
## ✖ purrr::map() masks maps::map()
## ✖ tidyr::pack() masks Matrix::pack()
## ✖ tidyr::unpack() masks Matrix::unpack()
## ℹ Use the conflicted package (<http://conflicted.r-lib.org/>) to force all conflicts to become errors
library(tigris)
## To enable caching of data, set `options(tigris_use_cache = TRUE)`
## in your R script or .Rprofile.
library(tmap)
## Breaking News: tmap 3.x is retiring. Please test v4, e.g. with
## remotes::install_github('r-tmap/tmap')
library(tmaptools)
library(viridis)
## Loading required package: viridisLite
##
## Attaching package: 'viridis'
##
## The following object is masked from 'package:scales':
##
## viridis_pal
##
## The following object is masked from 'package:maps':
##
## unemp
library(broom)
library(knitr)
library(dplyr)
#Load all data sets needed
d_popvote <- read_csv("popvote_1948_2020.csv")
## Rows: 40 Columns: 11
## ── Column specification ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
## Delimiter: ","
## chr (2): party, candidate
## dbl (5): year, pv, pv2p, deminc, juneapp
## lgl (4): winner, incumbent, incumbent_party, prev_admin
##
## ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data.
## ℹ Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.
d_state_popvote <- read_csv("state_popvote_1948_2020.csv")
## Rows: 959 Columns: 18
## ── Column specification ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
## Delimiter: ","
## chr (1): state
## dbl (17): year, D_pv, R_pv, D_pv2p, R_pv2p, votes_D, votes_R, total_votes, t...
##
## ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data.
## ℹ Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.
d_state_popvote[d_state_popvote$state == "District of Columbia",]$state <- "District Of Columbia"
d_ec <- read_csv("corrected_ec_1948_2024.csv")
## Rows: 1010 Columns: 4
## ── Column specification ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
## Delimiter: ","
## chr (2): state, stateab
## dbl (2): year, electors
##
## ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data.
## ℹ Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.
d_polls <- read_csv("national_polls_1968-2024.csv")
## Rows: 7474 Columns: 9
## ── Column specification ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
## Delimiter: ","
## chr (4): state, party, candidate, poll_date
## dbl (4): year, weeks_left, days_left, poll_support
## lgl (1): before_convention
##
## ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data.
## ℹ Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.
d_state_polls <- read_csv("state_polls_1968-2024.csv")
## Rows: 206608 Columns: 9
## ── Column specification ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
## Delimiter: ","
## chr (3): state, party, candidate
## dbl (4): year, weeks_left, days_left, poll_support
## lgl (1): before_convention
## date (1): poll_date
##
## ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data.
## ℹ Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.
d_turnout <- read_csv("state_turnout_1980_2022.csv")
## Rows: 1144 Columns: 15
## ── Column specification ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
## Delimiter: ","
## chr (5): state, vep_turnout, vep_highest_office, vap_highest_office, noncitizen
## dbl (1): year
## num (9): total_ballots, highest_office_ballots, vep, vap, prison, probation,...
##
## ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data.
## ℹ Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.
d_state_demog <- read_csv("demographics.csv")
## New names:
## Rows: 663 Columns: 44
## ── Column specification
## ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────── Delimiter: "," chr
## (1): state dbl (43): ...1, year, total_pop, white, black, american_indian,
## asian_pacifi...
## ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data. ℹ
## Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.
## • `` -> `...1`
d_state_gdp <- read_csv("cleaned_state_gdp.csv")
## New names:
## Rows: 969 Columns: 15
## ── Column specification
## ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────── Delimiter: "," chr
## (1): state dbl (14): ...1, year, Q4, Q3, Q2, Q1, Q2_prev_year, Q3_prev_year,
## Q2_4_year,...
## ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data. ℹ
## Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.
## • `` -> `...1`
d_state_unemployment <- read_csv("State_unemployment.csv")
## Rows: 52 Columns: 122
## ── Column specification ────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
## Delimiter: ","
## chr (3): State, Mar 2020, Apr 2020
## dbl (119): Sep 2014, Oct 2014, Nov 2014, Dec 2014, Jan 2015, Feb 2015, Mar 2...
##
## ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data.
## ℹ Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.
#Process state unemployment for my model's needs
#Making all columns except State numeric variables
d_state_unemployment[ , -1] <- lapply(d_state_unemployment[ , -1], as.numeric)
## Warning in lapply(d_state_unemployment[, -1], as.numeric): NAs introduced by
## coercion
## Warning in lapply(d_state_unemployment[, -1], as.numeric): NAs introduced by
## coercion
d_state_unemployment <- d_state_unemployment |>
pivot_longer(
cols = -State,
names_to = "date",
values_to = "unemployment" #as a rate
) |>
separate(date, into = c("month", "year"), sep = " ") |>
rename(state = State) |>
filter(month == "Sep")
d_state_unemployment$year <- as.numeric(d_state_unemployment$year)
d_state_unemployment
## # A tibble: 572 × 4
## state month year unemployment
## <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 Alabama Sep 2014 6.5
## 2 Alabama Sep 2015 6.1
## 3 Alabama Sep 2016 5.9
## 4 Alabama Sep 2017 4.1
## 5 Alabama Sep 2018 3.9
## 6 Alabama Sep 2019 3
## 7 Alabama Sep 2020 5.9
## 8 Alabama Sep 2021 3
## 9 Alabama Sep 2022 2.5
## 10 Alabama Sep 2023 2.7
## # ℹ 562 more rows
#Process gdp growth for model's need
d_state_gdp <- d_state_gdp |>
select(year, state, q2_gdp_growth)
d_state_gdp
## # A tibble: 969 × 3
## year state q2_gdp_growth
## <dbl> <chr> <dbl>
## 1 2005 Alabama NA
## 2 2005 Alaska NA
## 3 2005 Arizona NA
## 4 2005 Arkansas NA
## 5 2005 California NA
## 6 2005 Colorado NA
## 7 2005 Connecticut NA
## 8 2005 Delaware NA
## 9 2005 District of Columbia NA
## 10 2005 Florida NA
## # ℹ 959 more rows
d_state_demog <- d_state_demog |>
mutate(
# Create 'hispanic' column by summing all Hispanic race categories
hispanic = rowSums(d_state_demog[, c("hispanic_white", "hispanic_black", "hispanic_american_indian",
"hispanic_asian_pacific_islander", "hispanic_other_race",
"hispanic_two_or_more_races")], na.rm = TRUE),
# Create 'age_18_to_29' column by summing the relevant age groups
age_18_to_29 = rowSums(d_state_demog[, c("age_18_to_19", "age_20", "age_21",
"age_22_to_24", "age_25_to_29")], na.rm = TRUE),
# Create 'age_30_to_44' by summing the relevant age groups
age_30_to_44 = age_30_to_34 + age_35_to_44,
# Create 'age_55_to_64' by summing the relevant age groups
age_55_to_64 = age_55_to_59 + age_60_to_61 + age_62_to_64,
# Create 'age_75plus' by summing ages 75 and older
age_75plus = age_75_to_84 + age_85_and_over
)
d_state_demog
## # A tibble: 663 × 49
## ...1 year state total_pop white black american_indian
## <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 1 1972 Alabama 3534110. 73.6 26.1 0.105
## 2 2 1972 Alaska 320676. 78.6 3.06 7.54
## 3 3 1972 Arizona 1960363 89.1 2.96 5.46
## 4 4 1972 Arkansas 1995923 81.7 17.9 0.195
## 5 5 1972 California 20696088. 86.6 7.15 0.561
## 6 6 1972 Colorado 2343800 94.5 3.11 0.466
## 7 7 1972 Connecticut 3046882. 92.9 6.18 0.0901
## 8 8 1972 Delaware 557351. 84.5 14.7 0.143
## 9 9 1972 District of Columbia 732875. 27.6 70.9 0.133
## 10 10 1972 Florida 7380819. 84.2 15.0 0.130
## # ℹ 653 more rows
## # ℹ 42 more variables: asian_pacific_islander <dbl>, other_race <dbl>,
## # two_or_more_races <dbl>, hispanic_white <dbl>, hispanic_black <dbl>,
## # hispanic_american_indian <dbl>, hispanic_asian_pacific_islander <dbl>,
## # hispanic_other_race <dbl>, hispanic_two_or_more_races <dbl>,
## # not_hispanic_white <dbl>, not_hispanic_black <dbl>,
## # not_hispanic_american_indian <dbl>, …
# Process state-level polling data.
d_pollav_state <- d_state_polls |>
group_by(year, state, party) |>
mutate(mean_pollav = mean(poll_support, na.rm = TRUE)) |>
top_n(1, poll_date) |>
rename(latest_pollav = poll_support) |>
select(-c(weeks_left, days_left, poll_date, candidate, before_convention)) |>
pivot_wider(names_from = party, values_from = c(latest_pollav, mean_pollav))
# Merge data.
d <- d_pollav_state |>
left_join(d_state_popvote, by = c("year", "state")) |>
left_join(d_popvote |> filter(party == "democrat"), by = "year") |>
left_join(d_turnout, by = c("year", "state")) |>
left_join(d_state_unemployment, by = c("year", "state")) |>
left_join(d_state_gdp, by = c("year", "state")) |>
left_join(d_state_demog, by = c("state", "year")) |>
filter(year >= 1980) |>
ungroup() |>
distinct(state, year, .keep_all = TRUE)
d_turnout
## # A tibble: 1,144 × 15
## year state vep_turnout vep_highest_office vap_highest_office total_ballots
## <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
## 1 2022 United… 46.20% <NA> <NA> 112030874
## 2 2022 Alabama 37.30% <NA> <NA> 1424087
## 3 2022 Alaska 50.20% <NA> <NA> 267047
## 4 2022 Arizona 49.30% <NA> <NA> 2592313
## 5 2022 Arkans… 41.50% <NA> <NA> 914227
## 6 2022 Califo… 42.90% <NA> <NA> 11146610
## 7 2022 Colora… 58.30% <NA> <NA> 2540666
## 8 2022 Connec… 48.60% <NA> <NA> 1297811
## 9 2022 Delawa… 42.80% <NA> <NA> 325632
## 10 2022 Distri… 40.60% <NA> <NA> 205774
## # ℹ 1,134 more rows
## # ℹ 9 more variables: highest_office_ballots <dbl>, vep <dbl>, vap <dbl>,
## # noncitizen <chr>, prison <dbl>, probation <dbl>, parole <dbl>,
## # total_ineligible <dbl>, overseas_eligible <dbl>
# Sequester states for which we have polling data for 2024.
states.2024 <- unique(d$state[d$year == 2024])
states.2024 <- states.2024[-which(states.2024 == "Nebraska Cd 2")]
d <- d |>
filter(state %in% states.2024)
d
## # A tibble: 303 × 95
## year state latest_pollav_REP latest_pollav_DEM mean_pollav_REP
## <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 2016 Arizona 45.6 42.9 41.4
## 2 2016 California 32.8 54.9 31.7
## 3 2016 Colorado 40.8 43.6 41.4
## 4 2016 Florida 45.5 46.4 42.6
## 5 2016 Georgia 48.3 44.4 45.5
## 6 2016 Indiana 50.3 37.3 47.4
## 7 2016 Maryland 27.4 59.9 29.0
## 8 2016 Massachusetts 28.0 55.7 30.1
## 9 2016 Michigan 42.5 45.7 36.9
## 10 2016 Minnesota 38.1 47.0 39.0
## # ℹ 293 more rows
## # ℹ 90 more variables: mean_pollav_DEM <dbl>, D_pv <dbl>, R_pv <dbl>,
## # D_pv2p <dbl>, R_pv2p <dbl>, votes_D <dbl>, votes_R <dbl>,
## # total_votes <dbl>, two_party_votes <dbl>, D_pv_lag1 <dbl>, R_pv_lag1 <dbl>,
## # D_pv2p_lag1 <dbl>, R_pv2p_lag1 <dbl>, D_pv_lag2 <dbl>, R_pv_lag2 <dbl>,
## # D_pv2p_lag2 <dbl>, R_pv2p_lag2 <dbl>, party <chr>, winner <lgl>,
## # candidate <chr>, pv <dbl>, pv2p <dbl>, incumbent <lgl>, …
# Separate into training and testing for simple poll prediction model.
d.train <- d |> filter(year < 2024) |> select(year, state, D_pv2p, latest_pollav_DEM, D_pv2p_lag1, D_pv2p_lag2, q2_gdp_growth, white, black, american_indian, asian_pacific_islander, unemployment, less_than_college, bachelors, graduate, hispanic, age_18_to_29, age_30_to_44, age_45_to_54, age_55_to_64, age_65_to_74, age_75plus) |> drop_na() |> distinct(state, year, .keep_all = TRUE)
d.train
## # A tibble: 52 × 22
## year state D_pv2p latest_pollav_DEM D_pv2p_lag1 D_pv2p_lag2 q2_gdp_growth
## <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 2016 Arizona 48.1 42.9 45.4 45.7 2.67
## 2 2016 Califor… 66.1 54.9 61.9 62.3 1.88
## 3 2016 Colorado 52.7 43.6 52.7 54.6 1.57
## 4 2016 Florida 49.4 46.4 50.4 51.4 3.19
## 5 2016 Georgia 47.3 44.4 46.0 47.4 3.21
## 6 2016 Indiana 39.9 37.3 44.8 50.5 1.20
## 7 2016 Maryland 64.0 59.9 63.3 62.9 3.56
## 8 2016 Massach… 64.7 55.7 61.8 63.2 1.15
## 9 2016 Michigan 49.9 45.7 54.8 58.4 2.18
## 10 2016 Minneso… 50.8 47.0 53.9 55.2 1.35
## # ℹ 42 more rows
## # ℹ 15 more variables: white <dbl>, black <dbl>, american_indian <dbl>,
## # asian_pacific_islander <dbl>, unemployment <dbl>, less_than_college <dbl>,
## # bachelors <dbl>, graduate <dbl>, hispanic <dbl>, age_18_to_29 <dbl>,
## # age_30_to_44 <dbl>, age_45_to_54 <dbl>, age_55_to_64 <dbl>,
## # age_65_to_74 <dbl>, age_75plus <dbl>
d.test <- d |> filter(year == 2024) |> select(year, state, D_pv2p, latest_pollav_DEM, D_pv2p_lag1, D_pv2p_lag2, q2_gdp_growth, white, black, american_indian, asian_pacific_islander, unemployment, less_than_college, bachelors, graduate, hispanic, age_18_to_29, age_30_to_44, age_45_to_54, age_55_to_64, age_75plus) |> distinct(state, year, .keep_all = TRUE)
d.test
## # A tibble: 27 × 21
## year state D_pv2p latest_pollav_DEM D_pv2p_lag1 D_pv2p_lag2 q2_gdp_growth
## <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 2024 Arizona NA 46.4 NA NA 5.9
## 2 2024 Califor… NA 58.7 NA NA 5.4
## 3 2024 Colorado NA 52.8 NA NA 5.8
## 4 2024 Florida NA 44.5 NA NA 6.1
## 5 2024 Georgia NA 47.0 NA NA 6
## 6 2024 Indiana NA 39.2 NA NA 3.9
## 7 2024 Maine C… NA 43.7 NA NA NA
## 8 2024 Maryland NA 61.3 NA NA 5.1
## 9 2024 Massach… NA 59.7 NA NA 4.7
## 10 2024 Michigan NA 47.8 NA NA 6.5
## # ℹ 17 more rows
## # ℹ 14 more variables: white <dbl>, black <dbl>, american_indian <dbl>,
## # asian_pacific_islander <dbl>, unemployment <dbl>, less_than_college <dbl>,
## # bachelors <dbl>, graduate <dbl>, hispanic <dbl>, age_18_to_29 <dbl>,
## # age_30_to_44 <dbl>, age_45_to_54 <dbl>, age_55_to_64 <dbl>,
## # age_75plus <dbl>
# Step 1: Modify `t` to include demographic variables
t <- d |>
filter(year >= 2016) |>
arrange(year) |>
group_by(state) |>
mutate(
D_pv2p_lag1 = lag(D_pv2p, 1),
R_pv2p_lag1 = lag(R_pv2p, 1),
D_pv2p_lag2 = lag(D_pv2p, 2),
R_pv2p_lag2 = lag(R_pv2p, 2),
white = lag(white, 1),
black = lag(black, 1),
american_indian = lag(american_indian, 1),
asian_pacific_islander = lag(asian_pacific_islander, 1),
less_than_college = lag(less_than_college, 1),
bachelors = lag(bachelors, 1),
graduate = lag(graduate, 1),
hispanic = lag(hispanic, 1),
age_18_to_29 = lag(age_18_to_29, 1),
age_30_to_44 = lag(age_30_to_44, 1),
age_45_to_54 = lag(age_45_to_54, 1),
age_55_to_64 = lag(age_55_to_64, 1),
age_65_to_74 = lag(age_65_to_74, 1),
age_75plus = lag(age_75plus, 1)
) |>
filter(year == 2024) |>
select(state, year, D_pv2p, D_pv2p_lag1, R_pv2p_lag1, D_pv2p_lag2, R_pv2p_lag2, white, black, american_indian, asian_pacific_islander, less_than_college, bachelors, graduate, hispanic, age_18_to_29, age_30_to_44, age_45_to_54, age_55_to_64, age_65_to_74, age_75plus) |>
distinct(state, year, .keep_all = TRUE)
t
## # A tibble: 27 × 21
## # Groups: state [27]
## state year D_pv2p D_pv2p_lag1 R_pv2p_lag1 D_pv2p_lag2 R_pv2p_lag2 white
## <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 Arizona 2024 NA 50.2 49.8 48.1 51.9 60.4
## 2 California 2024 NA 64.9 35.1 66.1 33.9 41.2
## 3 Colorado 2024 NA 56.9 43.1 52.7 47.3 70.7
## 4 Florida 2024 NA 48.3 51.7 49.4 50.6 57.7
## 5 Georgia 2024 NA 50.1 49.9 47.3 52.7 51.9
## 6 Indiana 2024 NA 41.8 58.2 39.9 60.1 77.2
## 7 Maine Cd 2 2024 NA NA NA NA NA NA
## 8 Maryland 2024 NA 67.0 33.0 64.0 36.0 48.7
## 9 Massachus… 2024 NA 67.1 32.9 64.7 35.3 69.6
## 10 Michigan 2024 NA 51.4 48.6 49.9 50.1 73.9
## # ℹ 17 more rows
## # ℹ 13 more variables: black <dbl>, american_indian <dbl>,
## # asian_pacific_islander <dbl>, less_than_college <dbl>, bachelors <dbl>,
## # graduate <dbl>, hispanic <dbl>, age_18_to_29 <dbl>, age_30_to_44 <dbl>,
## # age_45_to_54 <dbl>, age_55_to_64 <dbl>, age_65_to_74 <dbl>,
## # age_75plus <dbl>
# Step 2: Join `t` with `d.test` to ensure demographic data is included for 2024 predictions
d.test <- d.test |>
left_join(t, by = c("state", "year"), suffix = c("", ".t")) |>
mutate(
D_pv2p_lag1 = ifelse(is.na(D_pv2p_lag1), D_pv2p_lag1.t, D_pv2p_lag1),
D_pv2p_lag2 = ifelse(is.na(D_pv2p_lag2), D_pv2p_lag2.t, D_pv2p_lag2),
D_pv2p = ifelse(is.na(D_pv2p), D_pv2p.t, D_pv2p),
# Include demographic variables with fallback values
white = ifelse(is.na(white), white.t, white),
black = ifelse(is.na(black), black.t, black),
american_indian = ifelse(is.na(american_indian), american_indian.t, american_indian),
asian_pacific_islander = ifelse(is.na(asian_pacific_islander), asian_pacific_islander.t, asian_pacific_islander),
less_than_college = ifelse(is.na(less_than_college), less_than_college.t, less_than_college),
bachelors = ifelse(is.na(bachelors), bachelors.t, bachelors),
graduate = ifelse(is.na(graduate), graduate.t, graduate),
hispanic = ifelse(is.na(hispanic), hispanic.t, hispanic),
age_18_to_29 = ifelse(is.na(age_18_to_29), age_18_to_29.t, age_18_to_29),
age_30_to_44 = ifelse(is.na(age_30_to_44), age_30_to_44.t, age_30_to_44),
age_45_to_54 = ifelse(is.na(age_45_to_54), age_45_to_54.t, age_45_to_54),
age_55_to_64 = ifelse(is.na(age_55_to_64), age_55_to_64.t, age_55_to_64),
age_75plus = ifelse(is.na(age_75plus), age_75plus.t, age_75plus),
) |>
select(-ends_with(".t"))
d.test
## # A tibble: 27 × 24
## year state D_pv2p latest_pollav_DEM D_pv2p_lag1 D_pv2p_lag2 q2_gdp_growth
## <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 2024 Arizona NA 46.4 50.2 48.1 5.9
## 2 2024 Califor… NA 58.7 64.9 66.1 5.4
## 3 2024 Colorado NA 52.8 56.9 52.7 5.8
## 4 2024 Florida NA 44.5 48.3 49.4 6.1
## 5 2024 Georgia NA 47.0 50.1 47.3 6
## 6 2024 Indiana NA 39.2 41.8 39.9 3.9
## 7 2024 Maine C… NA 43.7 NA NA NA
## 8 2024 Maryland NA 61.3 67.0 64.0 5.1
## 9 2024 Massach… NA 59.7 67.1 64.7 4.7
## 10 2024 Michigan NA 47.8 51.4 49.9 6.5
## # ℹ 17 more rows
## # ℹ 17 more variables: white <dbl>, black <dbl>, american_indian <dbl>,
## # asian_pacific_islander <dbl>, unemployment <dbl>, less_than_college <dbl>,
## # bachelors <dbl>, graduate <dbl>, hispanic <dbl>, age_18_to_29 <dbl>,
## # age_30_to_44 <dbl>, age_45_to_54 <dbl>, age_55_to_64 <dbl>,
## # age_75plus <dbl>, R_pv2p_lag1 <dbl>, R_pv2p_lag2 <dbl>, age_65_to_74 <dbl>
# Update the regression model to include demographic variables
reg.ols <- lm(D_pv2p ~ latest_pollav_DEM + D_pv2p_lag1 + D_pv2p_lag2 + q2_gdp_growth + white + black + american_indian + asian_pacific_islander + less_than_college + bachelors + graduate + hispanic + age_18_to_29 + age_30_to_44 + age_45_to_54 + age_55_to_64 + age_65_to_74 + age_75plus, data = d.train)
summary(reg.ols)
##
## Call:
## lm(formula = D_pv2p ~ latest_pollav_DEM + D_pv2p_lag1 + D_pv2p_lag2 +
## q2_gdp_growth + white + black + american_indian + asian_pacific_islander +
## less_than_college + bachelors + graduate + hispanic + age_18_to_29 +
## age_30_to_44 + age_45_to_54 + age_55_to_64 + age_65_to_74 +
## age_75plus, data = d.train)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -4.4888 -0.5383 0.0214 0.5888 2.1488
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) -10.00816 32.84308 -0.305 0.762488
## latest_pollav_DEM 0.54305 0.10863 4.999 1.85e-05 ***
## D_pv2p_lag1 0.03558 0.13000 0.274 0.786037
## D_pv2p_lag2 0.38624 0.10030 3.851 0.000513 ***
## q2_gdp_growth 0.02220 0.09086 0.244 0.808507
## white 0.31494 0.23272 1.353 0.185166
## black 0.26354 0.21702 1.214 0.233225
## american_indian 0.40327 0.33023 1.221 0.230664
## asian_pacific_islander 0.62921 0.36628 1.718 0.095200 .
## less_than_college -1.20374 1.34072 -0.898 0.375780
## bachelors -0.83998 1.37430 -0.611 0.545250
## graduate -0.55304 1.39483 -0.396 0.694291
## hispanic 0.24277 0.12554 1.934 0.061753 .
## age_18_to_29 1.45120 1.42208 1.020 0.314928
## age_30_to_44 0.22489 1.41381 0.159 0.874585
## age_45_to_54 2.00334 1.37929 1.452 0.155822
## age_55_to_64 -1.11776 1.84174 -0.607 0.548068
## age_65_to_74 2.71133 1.33194 2.036 0.049883 *
## age_75plus -0.22373 1.55950 -0.143 0.886800
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 1.378 on 33 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.9813, Adjusted R-squared: 0.9712
## F-statistic: 96.41 on 18 and 33 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16
pred.ols.dem <- predict(reg.ols, newdata = d.test)
pred.ols.dem
## 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
## 49.36694 66.02354 56.50472 45.34069 48.91996 38.15609 NA 64.60888
## 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
## 66.70648 47.78016 50.26365 38.17351 37.72057 37.82169 49.43660 50.82756
## 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
## 53.59671 61.88340 48.35522 42.23250 47.39012 41.76571 47.25647 40.13865
## 25 26 27
## 54.53748 59.49722 47.00644
library(glmnet)
library(dplyr)
# Assuming d.train and d.test are your training and testing datasets respectively
# Prepare your training data
x_train <- as.matrix(d.train[, c("latest_pollav_DEM", "D_pv2p_lag1", "D_pv2p_lag2", "white", "black", "american_indian", "asian_pacific_islander", "less_than_college", "bachelors", "graduate", "hispanic", "age_18_to_29", "age_30_to_44", "age_45_to_54", "age_55_to_64", "age_65_to_74", "age_75plus", "q2_gdp_growth")])
y_train <- d.train$D_pv2p
# Standardize predictors
x_train <- scale(x_train)
# Prepare your testing data
x_test <- as.matrix(d.test[, c("latest_pollav_DEM", "D_pv2p_lag1", "D_pv2p_lag2", "white", "black", "american_indian", "asian_pacific_islander", "less_than_college", "bachelors", "graduate", "hispanic", "age_18_to_29", "age_30_to_44", "age_45_to_54", "age_55_to_64", "age_65_to_74", "age_75plus", "q2_gdp_growth")])
x_test <- scale(x_test)
# Define a sequence of alpha values to try
alphas <- seq(0, 1, by = 0.1)
# Find the best alpha and lambda using cross-validation
results <- lapply(alphas, function(a) {
cv_fit <- cv.glmnet(x_train, y_train, alpha = a)
return(data.frame(alpha = a, lambda = cv_fit$lambda.min, cvm = min(cv_fit$cvm)))
})
# Convert results to a data frame
results_df <- do.call(rbind, results)
best_params <- results_df[which.min(results_df$cvm), ]
best_alpha <- best_params$alpha
best_lambda <- best_params$lambda
final_model <- glmnet(x_train, y_train, alpha = best_alpha, lambda = best_lambda)
# Make predictions using the Elastic Net model
predictions <- predict(final_model, newx = x_test, s = best_lambda)
pred_elastic_net <- as.vector(predictions)
results <- data.frame(
state = d.test$state,
predicted_D_pv2p = pred_elastic_net,
predicted_winner = ifelse(pred_elastic_net > 50, "Democrat", "Republican")
)
# Filter results for specific states
final_results <- results %>%
filter(state %in% c("Arizona", "Georgia", "Michigan", "Nevada", "North Carolina", "Pennsylvania", "Wisconsin"))
print(final_results)
## state predicted_D_pv2p predicted_winner
## 1 Arizona 50.55875 Democrat
## 2 Georgia 50.32704 Democrat
## 3 Michigan 49.31514 Republican
## 4 Nevada 50.70580 Democrat
## 5 North Carolina 49.75490 Republican
## 6 Pennsylvania 48.58076 Republican
## 7 Wisconsin 48.31193 Republican
# correlation matrix for model variables
cor_matrix <- cor(d.train[, c("latest_pollav_DEM", "D_pv2p_lag1", "D_pv2p_lag2", "white", "black", "american_indian", "asian_pacific_islander", "less_than_college", "bachelors", "graduate", "hispanic", "age_18_to_29", "age_30_to_44", "age_45_to_54", "age_55_to_64", "age_65_to_74", "age_75plus", "q2_gdp_growth")])
print(cor_matrix)
## latest_pollav_DEM D_pv2p_lag1 D_pv2p_lag2 white
## latest_pollav_DEM 1.0000000 0.83392805 0.70218567 -0.48180317
## D_pv2p_lag1 0.8339280 1.00000000 0.92244118 -0.44992859
## D_pv2p_lag2 0.7021857 0.92244118 1.00000000 -0.29780877
## white -0.4818032 -0.44992859 -0.29780877 1.00000000
## black 0.1933139 0.14117914 0.10962505 -0.48727823
## american_indian -0.1049692 -0.04590781 -0.04605956 -0.11518521
## asian_pacific_islander 0.6391178 0.67470872 0.57017516 -0.60471235
## less_than_college -0.4005134 -0.26889920 -0.13748743 0.02410127
## bachelors 0.5102479 0.36843374 0.29998466 0.19229910
## graduate 0.7545521 0.67563547 0.59834530 -0.19100817
## hispanic 0.1663259 0.21975390 0.09455487 -0.68099441
## age_18_to_29 -0.1962627 -0.19739595 -0.31557399 -0.12548014
## age_30_to_44 0.1590385 0.19637900 0.04249750 -0.51831317
## age_45_to_54 0.2311597 0.54264180 0.62415381 -0.03657881
## age_55_to_64 0.2764114 0.27901154 0.43490082 0.34085812
## age_65_to_74 0.2146674 0.06350367 0.14573155 0.11489596
## age_75plus 0.1555921 0.15512982 0.26179444 0.21295083
## q2_gdp_growth -0.3932084 -0.01743752 -0.01706968 0.11954415
## black american_indian asian_pacific_islander
## latest_pollav_DEM 0.19331390 -0.1049692038 0.63911778
## D_pv2p_lag1 0.14117914 -0.0459078141 0.67470872
## D_pv2p_lag2 0.10962505 -0.0460595637 0.57017516
## white -0.48727823 -0.1151852123 -0.60471235
## black 1.00000000 -0.4197600789 0.05622805
## american_indian -0.41976008 1.0000000000 -0.20998016
## asian_pacific_islander 0.05622805 -0.2099801618 1.00000000
## less_than_college 0.06720393 0.1959565836 -0.35263269
## bachelors -0.15391544 -0.2609137668 0.27150794
## graduate 0.17903018 -0.1650380170 0.38614431
## hispanic -0.21197723 0.4972419477 0.37501039
## age_18_to_29 -0.17133511 0.0258686401 0.18817228
## age_30_to_44 0.05947731 -0.1232637144 0.58541806
## age_45_to_54 0.38936719 -0.3899164222 0.16889804
## age_55_to_64 0.02785193 0.0009966614 -0.22602836
## age_65_to_74 0.01146534 0.2341464921 -0.29778231
## age_75plus -0.04135942 0.0785925383 -0.24307132
## q2_gdp_growth -0.02835996 0.0054563007 -0.07637543
## less_than_college bachelors graduate hispanic
## latest_pollav_DEM -0.40051344 0.51024790 0.75455206 0.16632587
## D_pv2p_lag1 -0.26889920 0.36843374 0.67563547 0.21975390
## D_pv2p_lag2 -0.13748743 0.29998466 0.59834530 0.09455487
## white 0.02410127 0.19229910 -0.19100817 -0.68099441
## black 0.06720393 -0.15391544 0.17903018 -0.21197723
## american_indian 0.19595658 -0.26091377 -0.16503802 0.49724195
## asian_pacific_islander -0.35263269 0.27150794 0.38614431 0.37501039
## less_than_college 1.00000000 -0.77506811 -0.70719759 0.06057206
## bachelors -0.77506811 1.00000000 0.72786388 -0.26957882
## graduate -0.70719759 0.72786388 1.00000000 -0.08327055
## hispanic 0.06057206 -0.26957882 -0.08327055 1.00000000
## age_18_to_29 -0.40190802 -0.03134756 -0.03546023 0.28574164
## age_30_to_44 -0.45973842 0.15669127 0.09768318 0.45927148
## age_45_to_54 0.11172642 0.14807754 0.31779866 -0.25132395
## age_55_to_64 0.27799876 0.24849211 0.27268675 -0.44865171
## age_65_to_74 0.47058418 0.02422522 0.06270197 -0.16164107
## age_75plus 0.43024997 0.02368186 0.09820635 -0.18274175
## q2_gdp_growth -0.01436552 -0.15902956 -0.16325610 0.02800824
## age_18_to_29 age_30_to_44 age_45_to_54 age_55_to_64
## latest_pollav_DEM -0.19626266 0.15903847 0.23115975 0.2764113834
## D_pv2p_lag1 -0.19739595 0.19637900 0.54264180 0.2790115414
## D_pv2p_lag2 -0.31557399 0.04249750 0.62415381 0.4349008219
## white -0.12548014 -0.51831317 -0.03657881 0.3408581233
## black -0.17133511 0.05947731 0.38936719 0.0278519275
## american_indian 0.02586864 -0.12326371 -0.38991642 0.0009966614
## asian_pacific_islander 0.18817228 0.58541806 0.16889804 -0.2260283587
## less_than_college -0.40190802 -0.45973842 0.11172642 0.2779987605
## bachelors -0.03134756 0.15669127 0.14807754 0.2484921124
## graduate -0.03546023 0.09768318 0.31779866 0.2726867513
## hispanic 0.28574164 0.45927148 -0.25132395 -0.4486517054
## age_18_to_29 1.00000000 0.53539057 -0.39620648 -0.7799927132
## age_30_to_44 0.53539057 1.00000000 -0.09254776 -0.7091768651
## age_45_to_54 -0.39620648 -0.09254776 1.00000000 0.4932061691
## age_55_to_64 -0.77999271 -0.70917687 0.49320617 1.0000000000
## age_65_to_74 -0.73072234 -0.68095319 0.09080440 0.7888722857
## age_75plus -0.68796830 -0.75537744 0.22130697 0.7228140433
## q2_gdp_growth 0.28873057 0.24663837 0.29868296 -0.3266608698
## age_65_to_74 age_75plus q2_gdp_growth
## latest_pollav_DEM 0.21466738 0.15559207 -0.393208389
## D_pv2p_lag1 0.06350367 0.15512982 -0.017437516
## D_pv2p_lag2 0.14573155 0.26179444 -0.017069682
## white 0.11489596 0.21295083 0.119544149
## black 0.01146534 -0.04135942 -0.028359963
## american_indian 0.23414649 0.07859254 0.005456301
## asian_pacific_islander -0.29778231 -0.24307132 -0.076375427
## less_than_college 0.47058418 0.43024997 -0.014365516
## bachelors 0.02422522 0.02368186 -0.159029557
## graduate 0.06270197 0.09820635 -0.163256104
## hispanic -0.16164107 -0.18274175 0.028008238
## age_18_to_29 -0.73072234 -0.68796830 0.288730566
## age_30_to_44 -0.68095319 -0.75537744 0.246638368
## age_45_to_54 0.09080440 0.22130697 0.298682957
## age_55_to_64 0.78887229 0.72281404 -0.326660870
## age_65_to_74 1.00000000 0.81187914 -0.486376631
## age_75plus 0.81187914 1.00000000 -0.229458740
## q2_gdp_growth -0.48637663 -0.22945874 1.000000000
# Calculate VIF to check for multicollinearity
library(car)
## Loading required package: carData
##
## Attaching package: 'car'
## The following object is masked from 'package:dplyr':
##
## recode
## The following object is masked from 'package:purrr':
##
## some
vif_model <- vif(lm(D_pv2p ~ latest_pollav_DEM + D_pv2p_lag1 + D_pv2p_lag2 + q2_gdp_growth + white + black + american_indian + asian_pacific_islander + less_than_college + bachelors + graduate + hispanic + age_18_to_29 + age_30_to_44 + age_45_to_54 + age_55_to_64 + age_65_to_74 + age_75plus, data = d.train))
print(vif_model)
## latest_pollav_DEM D_pv2p_lag1 D_pv2p_lag2
## 18.63658 31.88611 16.81634
## q2_gdp_growth white black
## 6.15531 219.05611 88.92473
## american_indian asian_pacific_islander less_than_college
## 13.60474 35.86533 581.29787
## bachelors graduate hispanic
## 193.21365 197.15273 62.88381
## age_18_to_29 age_30_to_44 age_45_to_54
## 33.14366 50.42852 43.89433
## age_55_to_64 age_65_to_74 age_75plus
## 113.40627 59.06835 60.93673
win_pred <- data.frame(state = d.test$state,
year = rep(2024, length(d.test$state)),
simp_pred_dem = pred.ols.dem,
simp_pred_rep = 100 - pred.ols.dem) |>
mutate(winner = ifelse(simp_pred_dem > simp_pred_rep, "Democrat", "Republican")) |>
left_join(d_ec, by = c("state", "year"))
win_pred
## state year simp_pred_dem simp_pred_rep winner stateab electors
## 1 Arizona 2024 49.36694 50.63306 Republican AZ 11
## 2 California 2024 66.02354 33.97646 Democrat CA 54
## 3 Colorado 2024 56.50472 43.49528 Democrat CO 10
## 4 Florida 2024 45.34069 54.65931 Republican FL 30
## 5 Georgia 2024 48.91996 51.08004 Republican GA 16
## 6 Indiana 2024 38.15609 61.84391 Republican IN 11
## 7 Maine Cd 2 2024 NA NA <NA> <NA> NA
## 8 Maryland 2024 64.60888 35.39112 Democrat MD 10
## 9 Massachusetts 2024 66.70648 33.29352 Democrat MA 11
## 10 Michigan 2024 47.78016 52.21984 Republican MI 15
## 11 Minnesota 2024 50.26365 49.73635 Democrat MN 10
## 12 Missouri 2024 38.17351 61.82649 Republican MO 10
## 13 Montana 2024 37.72057 62.27943 Republican MT 4
## 14 Nebraska 2024 37.82169 62.17831 Republican NE 5
## 15 Nevada 2024 49.43660 50.56340 Republican NV 6
## 16 New Hampshire 2024 50.82756 49.17244 Democrat NH 4
## 17 New Mexico 2024 53.59671 46.40329 Democrat NM 5
## 18 New York 2024 61.88340 38.11660 Democrat NY 28
## 19 North Carolina 2024 48.35522 51.64478 Republican NC 16
## 20 Ohio 2024 42.23250 57.76750 Republican OH 17
## 21 Pennsylvania 2024 47.39012 52.60988 Republican PA 19
## 22 South Carolina 2024 41.76571 58.23429 Republican SC 9
## 23 Texas 2024 47.25647 52.74353 Republican TX 40
## 24 Utah 2024 40.13865 59.86135 Republican UT 6
## 25 Virginia 2024 54.53748 45.46252 Democrat VA 13
## 26 Washington 2024 59.49722 40.50278 Democrat WA 12
## 27 Wisconsin 2024 47.00644 52.99356 Republican WI 10
win_pred |>
filter(winner == "Democrat") |>
select(state)
## state
## 1 California
## 2 Colorado
## 3 Maryland
## 4 Massachusetts
## 5 Minnesota
## 6 New Hampshire
## 7 New Mexico
## 8 New York
## 9 Virginia
## 10 Washington
win_pred |>
filter(winner == "Republican") |>
select(state)
## state
## 1 Arizona
## 2 Florida
## 3 Georgia
## 4 Indiana
## 5 Michigan
## 6 Missouri
## 7 Montana
## 8 Nebraska
## 9 Nevada
## 10 North Carolina
## 11 Ohio
## 12 Pennsylvania
## 13 South Carolina
## 14 Texas
## 15 Utah
## 16 Wisconsin
win_pred |>
group_by(winner) |>
summarize(n = n(), ec = sum(electors))
## # A tibble: 3 × 3
## winner n ec
## <chr> <int> <dbl>
## 1 Democrat 10 157
## 2 Republican 16 225
## 3 <NA> 1 NA
# Create data set to summarize winners and EC
win_pred <- data.frame(state = d.test$state,
year = rep(2024, length(d.test$state)),
simp_pred_dem = pred.ols.dem,
simp_pred_rep = 100 - pred.ols.dem) |>
mutate(winner = ifelse(simp_pred_dem > simp_pred_rep, "Democrat", "Republican")) |> left_join(d_ec, by = c("state", "year"))
#### monte carlo simulations so i can create confidence intervals
# Set the number of simulations
m <- 1e4 # 10,000 simulations
residual_se <- summary(reg.ols)$sigma
pred_dem <- predict(reg.ols, newdata = d.test)
n_states <- nrow(d.test)
pred.mat <- data.frame(
state = rep(d.test$state, times = m),
year = rep(2024, times = m * n_states),
simp_pred_dem = numeric(m * n_states),
simp_pred_rep = numeric(m * n_states)
)
j <- 1
for (i in 1:m) {
if (i %% 1000 == 0) {
print(paste("Simulation", i))
}
simulated_errors <- rnorm(n_states, mean = 0, sd = residual_se)
pred_dem_sim <- pred_dem + simulated_errors
pred_dem_sim <- pmin(pmax(pred_dem_sim, 0), 100)
pred_rep_sim <- 100 - pred_dem_sim
idx <- j:(i * n_states)
pred.mat$simp_pred_dem[idx] <- pred_dem_sim
pred.mat$simp_pred_rep[idx] <- pred_rep_sim
j <- j + n_states
}
## [1] "Simulation 1000"
## [1] "Simulation 2000"
## [1] "Simulation 3000"
## [1] "Simulation 4000"
## [1] "Simulation 5000"
## [1] "Simulation 6000"
## [1] "Simulation 7000"
## [1] "Simulation 8000"
## [1] "Simulation 9000"
## [1] "Simulation 10000"
pred.mat <- pred.mat %>%
mutate(
winner = ifelse(simp_pred_dem > simp_pred_rep, "Democrat", "Republican")
)
####
electoral_outcomes <- pred.mat |>
group_by(state) |>
summarize(
mean_dem = mean(simp_pred_dem),
mean_rep = mean(simp_pred_rep),
sd_dem = sd(simp_pred_dem),
sd_rep = sd(simp_pred_rep),
lower_dem = mean_dem - 1.96 * sd_dem,
upper_dem = mean_dem + 1.96 * sd_dem,
lower_rep = mean_rep - 1.96 * sd_rep,
upper_rep = mean_rep + 1.96 * sd_rep
) |>
mutate(
winner = ifelse(mean_dem > mean_rep, "Democrat", "Republican")
)
view(electoral_outcomes)
#Since this only gives us the results for 19 states, it includes all swing states so a simple calculation with lagged vote will allow me to fill in the winner for the rest of the US
#list of all states
all_states <- state.name
missing_states <- setdiff(all_states, unique(electoral_outcomes$state))
missing_states
## [1] "Alabama" "Alaska" "Arkansas" "Connecticut"
## [5] "Delaware" "Hawaii" "Idaho" "Illinois"
## [9] "Iowa" "Kansas" "Kentucky" "Louisiana"
## [13] "Maine" "Mississippi" "New Jersey" "North Dakota"
## [17] "Oklahoma" "Oregon" "Rhode Island" "South Dakota"
## [21] "Tennessee" "Vermont" "West Virginia" "Wyoming"
#created a new data frame for the missing states
missing_data <- d_state_popvote |>
filter(state %in% missing_states) |>
filter(year == 2020) |>
select(state, D_pv2p_lag1, R_pv2p_lag1)
#Create the winner column based on lagged vote shares. Since these are not swing states, using the outcome from the last election reflects whethere it is a blue/red state
missing_data <- missing_data|>
mutate(
winner = ifelse(D_pv2p_lag1 > R_pv2p_lag1, "Democrat", "Republican")
)
ec_2024 <- d_ec |>
filter(year == 2024) |>
select(state, electors)
#Combine datasets
all_states_pred <- bind_rows(electoral_outcomes, missing_data) |>
left_join(ec_2024, by = "state")
winner <- all_states_pred |>
group_by(winner) |>
summarize(total_electors = sum(electors))
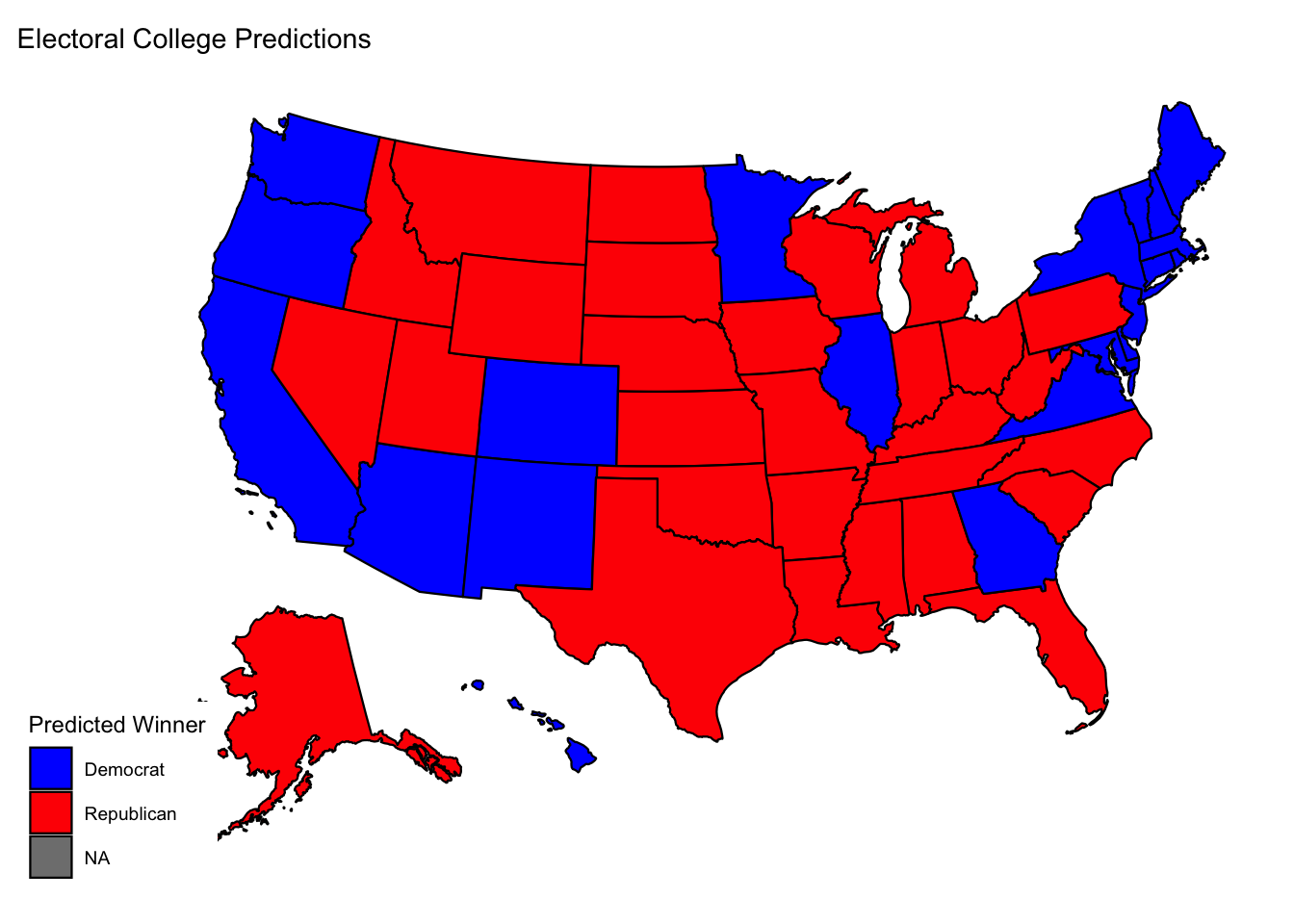
winner
## # A tibble: 3 × 2
## winner total_electors
## <chr> <dbl>
## 1 Democrat 223
## 2 Republican 312
## 3 <NA> NA
#DC not included so add 3 for Dem electoral college count
election_results <- tibble(
party = c("Democrat", "Republican"),
total_electors = c(winner$total_electors[1] + 3, winner$total_electors[2])
)
kable(election_results)
| party | total_electors |
|---|
| Democrat | 226 |
| Republican | 312 |
plot_usmap(data = all_states_pred, regions = "states", values = "winner") + scale_fill_manual(
values = c("Democrat" = "blue", "Republican" = "red"),
name = "Predicted Winner"
) +
labs(title = "Electoral College Predictions")
#how close is this race?
electoral_outcomes_close <- electoral_outcomes |>
filter(state %in% c("Arizona", "Georgia", "Michigan", "Nevada", "North Carolina", "Pennsylvania", "Wisconsin")) |>
select(state, mean_dem, mean_rep, lower_dem, upper_dem,lower_rep, upper_rep, winner)
kable(electoral_outcomes_close)
| state | mean_dem | mean_rep | lower_dem | upper_dem | lower_rep | upper_rep | winner |
|---|
| Arizona | 49.37393 | 50.62607 | 46.69963 | 52.04824 | 47.95176 | 53.30037 | Republican |
| Georgia | 48.92008 | 51.07992 | 46.18223 | 51.65792 | 48.34208 | 53.81777 | Republican |
| Michigan | 47.76604 | 52.23396 | 45.05198 | 50.48009 | 49.51991 | 54.94802 | Republican |
| Nevada | 49.43468 | 50.56532 | 46.74295 | 52.12642 | 47.87358 | 53.25705 | Republican |
| North Carolina | 48.37044 | 51.62956 | 45.66500 | 51.07588 | 48.92412 | 54.33500 | Republican |
| Pennsylvania | 47.40134 | 52.59866 | 44.72298 | 50.07971 | 49.92029 | 55.27702 | Republican |
| Wisconsin | 47.00512 | 52.99488 | 44.29103 | 49.71922 | 50.28078 | 55.70897 | Republican |
